In simple terms the question we are asking is "Given an unsorted array of elements, return all elements where the value of the element is greater than half of the values in the array."
So for example, given an array of the elements [7,3,5,8], return 7 and 8. In the case of an odd array, do not return the tied value, so an array such as [11,4,7,9,2], you would return 9 and 11, with 7 being the middle value.
Just thinking about it, the immediate answer that springs to mind is to take each value of the array and iterate over each other value of the array and count how many of them are smaller than the current number, if your count of numbers smaller than the current number is greater than half the length of the array, you can just add that number to the array you're going to return. That solution would look something like this
Except... that's not a very good solution. It'll run in O(n^2) time. Yuck. We don't like n^2 solutions, because they're very time consuming. Imagine if your array had a million numbers? It would take minutes to solve!
A better approach might be to consider this, the biggest half of elements would just be the first half of a sorted array! Thus if we want to make this problem trivial, all we need to do is come up with an efficient way of sorting the array, and then take half of it! I'm personally a big fan of the merge sort, but you would get the same result with a pivot sort or a quick sort. Simply sort the array, and then take the left half of it. The solution might look something like this:
This is a much better solution, with a runtime of O(nlogn). A better sort would give us a shorter time.
Some basic benchmarking, with an array with a ten thousand elements, the naive solution takes: 10 seconds, while the non-naive solution takes: 0.03. Quite a difference! This becomes more obvious in the 100,000 element array, where the naive solution takes: 834 seconds, almost 15 minutes, while the optimal solution takes 0.4 seconds!
The core takeaway of this algorithm is to always consider sorting unordered arrays when given a problem that deals with comparing values.
Sunday, December 11, 2016
Sunday, November 27, 2016
Finding Challenges
This blog post is going to be a little less technical than I would like, but it touches on a topic that I think every aspiring developer should think on, hard an often. That question is "what should I build?". Its a difficult question, because as you acquire new skills its easy to find a million applications that would be too difficult to implement, or another half a million which are too easy. Googling for "problems for aspiring developers" or even "practice problems" isn't very helpful. Having gone though this extensively, I have found out a number of approaches. The key is to find which, if any, work for you.
Coding Challenges
This is a typically offered solution. There are many websites out there like leetcode, project euler, hacker rank, interviewcake and codeeval that offer what they usually refer to as coding interview prep questions, and if your main goal is to land a job, you will probably learn a lot of specifically useful things, as well as how to think of specific problems to find clever solutions. There are a lot of problems, and its unlikely you'll transcend what these sites have to offer for a long time. The focus on sticking to the core of your language, with no fancy gems or extraneous tools can really serve to ground you in reality and teach you the finer details of your core skills.
These benefits come with a few drawbacks. Its hard to showcase on a resume, and while some sites, such as hacker rank offer a score you can show, unless its truly impressive its probably not something an interviewer is going to care about excessively. It also doesn't really teach you what building big, full fleshed projects feels like, and leaves you stranded in the land of your specific language, rather than bringing in interesting frameworks, and new tools.
If you like puzzles though, Coding challenges will provide small bite sized doses that provide a tangible feeling of progress, and that's important.
Build for yourself
We all have it, the dream project we all have wanted to build, maybe its something that's been built and implemented often, like Conway's Game of Life, or a simple maze program. Or maybe its more ambitious, like a fully fledged simulation of the behavior of twitter users, or a method to get push notifications whenever someone posts on a forum you like. Whatever it is, take this project and break it down into its component parts. Figure out the details, break down what you need to learn how to do, and what you know what to do. Then build it. Start with the smallest parts, and learn what you don't know. An evening of messing around with a database can teach you more than reading a few thousand words on it, and you won't know how to properly build routes until someone comes along and breaks the website you so cleverly crafted. This will teach you many things, be it deployment, or database usage, as well as training you on the number one thing every programmer needs to know. How to learn. You will break things. Things will not work, but you will learn.
This comes with a few drawbacks as well. A lot of what you'll learn is not immediately applicable. You'll run into paywalls and insurmountable problems. Getting a product you're satisfied with takes time. Your github account may wind up littered with the corpses of half finished programs, perhaps discouraging interviewers who don't understand the walls and limitations you've hit. Your raspeberry pi will catch fire when you screw something up badly enough. Interviewers won't care what you've built if you can't figure out reversing a linked list.
Most people who learn to code do so out of a desire to build. If building is your thing, then *build*, you'll be the better for it.
Build for others
I once read on a stack overflow question, that the best way to learn was to go out there and find problems people needed solving, and to figure out how to solve them. Its taken me some time and a growth in my skills to realize that even a very junior coder has skills very few people have and that problems that seem very difficult can be almost trivial with the right tools. When you're done building all your side projects, or when they've grown burdensome, or if you simply don't have anything you really want to build for *you*, go out and find problems that need solving. Earlier this week, i discovered that a certain forum I like has no good working mobile app, and no push notifications. I set out to try to figure out solutions to these problems. Will I build a killer app? Probably not, but I might use twilio to replicate push notifications for interested users. This has many of the same benefits as building for yourself, with the added benefit of teaching you what interacting with real users and their nebulous requirements is actually like
This is not free of burdens. Some problems haven't been solved because they are very hard to solve, or because the owner of the product doesn't wish to fix the issues. Sometimes you'll run into the real issue of hosting and maintaining a product other people use, and problems of ethics. You may find that what you've built relies on others, and doesn't last, consigning your hard work to obscurity and uselessness
The bottom line, is that with some basic coding skills, you can tackle problems others find impossible. By doing so, you can learn more, and have actual deployed projects to show interviewers.
Conclusion
This is not an exclusive list by any means, just a resource I wish I'd had when I started googling around for answers to this question. Some or all of these methods may not work for you, they're simply what work for me. At the very least, you should be asking "what can I do?", and if you are, you're already on the right track.
Sunday, November 20, 2016
Reddit API: The gateway to data
Reddit API: The gateway to data
An important note to consider when reading this. While these are all theoretical implementations, if I can conceive of them, I guarantee you, there are people who have already implemented these, be they individuals who are curious about the flow of data, or companies trying to leverage the power of advertising. What we post on the internet is public domain, and a lot can be extrapolated from patterns of behavior. The mere fact that Reddit uses a popularity system to determine the viewership of posts makes it an especially juicy target for large scale data mining.
Example 1: Deep User Analysis
The tool I wrote to profile users is deliberately quite tame. It doesn't for example, see where an user is geographically located. Or what their gender is. Or what age group they belong to. But those are all very easy to determine, unless the poster is exceedingly careful about the type of information they choose to share.It is, for starters, trivially easy to pull out the exact date of every post an user makes. With that, you can generally chart their timezone, or at the very least, times in which they are up. Further, you could trivially check the content of all their posts for key words, such as cities, to determine where they live, or brands, to determine hobbies and interests. While this method would absolutely not be fool proof, with a little machine learning and some data smoothing, I predict you could get at least a 90% guess on where a particular user lives, what their gender is, and what age group they belong to, assuming they had enough posts to go on.
But it doesn't stop there. While its easy to figure out the status of an user, that by itself seems impractical, after all, expending all this effort to profile a single user is, frankly a waste of time. Which brings us to my second point
Example 2: Subreddit Profiling
A super simple application of Deep User Analysis is to profile the population of a subreddit. Let say, for example, that a make up company wishes to see how well their product does in /r/makeupaddiction, a subreddit focused on makeup. It would be trivial for them to monitor for new posts containing their product name, for example, by simply organizing a search targeted at that subreddit sorting by new and containing the specific keyword. It would look something like this. That would be trivial to do, with even a small server running on a rasberry pi, that could be checked manually every day. But, assuming this company can spend a little more money, they could upgrade, beyond just gathering data of direct mentions in posts.
A sample implementation would go like this. Set up a bot to check whenever anything new is posted to r/makeup addiction. Keep track of that post for 48 hours via a database. After 48 hours it'll have dropped from the rankings, measure its popularity. For posts that pass a certain threshold, run a Deep User Analysis on each user, further checking the thread for positive and negative reactions based on some simple NLP (or, if you'd rather not deal with Markov chains, get an intern to go over posts that meet parameters such as mentioning your company or a competing company.). Suddenly you have a vast swathe of data. How your product is perceived, who uses it, what demographics they fall into. All it cost you was one skilled developer and some server time. Maybe an intern too, if your developer is busy with other projects.
If you're particularly nefarious and unprincipled, you can then task the selfsame intern to do some astroturfing. At the very least your company has a better handle on who uses their products, and can definitively measure the effect of targeted advertising.
Example 3: Influencing Reddit
This goes into the unethical, but completely possible. Reddit API allows for remote management of user accounts. As we just showed, its trivial to implement monitoring of new posts by keyword. What does this mean? It means that its relatively trivial to program a downvote bot. In fact, with maybe 20 bots, and a little creativity, you could dominate the discourse of a particular subreddit, especially one with a small moderation team. I'm sure its something reddit admins have controls in place for, but realistically, it would be very difficult to distinguish between legitimate uses of the API and uses that allow users to be malicious like this.
The api rules say "Note: votes must be cast by humans. That is, API clients proxying a human's action one-for-one are OK, but bots deciding how to vote on content or amplifying a human's vote are not. See the reddit rules for more details on what constitutes vote cheating.". I can't see this stopping anyone with money on the line, as changing your IP and getting a new API key is as easy as paying 15 dollars a month for a VPN, and having an intern to generate new accounts, if you can't find your way around a capcha.
The bottom line is given the ease of implementing a vote manipulation bot, a sufficiently unprincipled group could easily reduce the visibility of posts by the competition.
Conclusion
These are only some of the potential uses of the Reddit API, a simple, logical chain of things that can be done with only basic functionality. This is without diving deep into some of the more convoluted ways you might manipulate Reddit, or gather data on it, if you had enough resources (like, for example a government or major corporation). There are *some* limitations to the Reddit API, like the 6000 calls per minute limit, and the fact that it only returns the last 1000 contributions by author, but its important to realize that despite these limitations, the Reddit API holds incredible power.
I would never suggest we quit using Reddit altogether, or even that we obfuscate what we post, this is simply a reminder that yes, what you post is public, and that with such powerful tools and big payouts, people will use that data. This is not a problem exclusive to Reddit. Any place where data is published in a publicly accessible manner can, and will, be data mined.
Sunday, November 13, 2016
Basic Algorithms: The Duplicate Number
As part of learning to code, it is important to learn how to think about certain problems, specifically simple algorithm problems.
The Problem
You have an array of numbers from 1 to n-1, one of the numbers is duplicated, meaning the array has a length of n. For example
[1,2,3,3,4,5,6,7], where the duplicates is 3.
The array is not necessarily sorted. Find and return the duplicated number.
Another sample array might be
[4,2,3,2,1,5,6]. with 2 being a duplicate
The Naive Solution
A naive solution, that is, one not optimized for memory or computational savings, would likely do something along the lines of,
- Create a comparison array, which is a duplicate of the first array
- Delete the first number from the comparison array.
- Compare the first number of the main array to each value in the comparison array
- If it matches any numbers in the comparison array, it is our duplicate, return it
- If it doesn't, delete that number from the first array.
- Repeat for each number until you have the duplicate
This is obviously not terribly efficient, with a space complexity of O(n), as it requires a new array to be created (two if you want to back up the main array), and a time complexity of O(n^2) as you iterate over a number of arrays. It is not a good solution, but it would work.
The code would look something like this
The Optimized Solution
This can actually be solved with a time complexity of O(n) and a space complexity of O(1). Given that the array has a known length, n, and that the digits only go up to n-1, we can figure out what we would expect the sum of an array of no duplicates to look like, and then subtract the sum of the original array from the theoretical array. This requires iterating over the first array only once to sum it.
In testing, using an array of 1,000,000, digits the optimal solution took about 0.1 second to run, (on an average of 10 trials) while the naive version took 45 seconds. The 10,000,000 trial took one second in the optimized version, and 414(!) seconds (almost 7 minutes) in the naive version. In the 100,000,000 number trial, the optimized version took roughly 10 seconds. I did not run the naive version as the projected time to run would be 414 seconds squared, which is roughly two days! This should highlight the importance of efficient search algorithms in managing large data sets.
In testing, using an array of 1,000,000, digits the optimal solution took about 0.1 second to run, (on an average of 10 trials) while the naive version took 45 seconds. The 10,000,000 trial took one second in the optimized version, and 414(!) seconds (almost 7 minutes) in the naive version. In the 100,000,000 number trial, the optimized version took roughly 10 seconds. I did not run the naive version as the projected time to run would be 414 seconds squared, which is roughly two days! This should highlight the importance of efficient search algorithms in managing large data sets.
The important takeaway here is that, by thinking of the constraints of the problem, it is possible to arrive at a better solution. With algorithm questions, the elegant solutions most often rely on finding the way the limitations of the data set can be leveraged.
Sunday, November 6, 2016
Ruby 101: Objects and Method Calls
One of the biggest conceptual jumps between being a "for fun" coder that works on small side projects, and being someone who codes frequently and tackles difficult projects, is really understanding what goes on "under the hood" so to speak.
The most important thing to get, and something that takes a while to get a handle on at first, is that in ruby, everything is an object. Everything. Not just the thing you made a class out of, but everything you use. When you define a variable, that variable points to an object. When you create an array, that array is an object.
More importantly, every object belongs to a class. Read that again. Every object belongs to a class. If you go far up the chain, every object actually inherits from the Object class, which in turn inherits from the BasicObject class. So really, when we say "everything in ruby is an object" we mean, "everything in ruby inherits from the Object class".
This is super easy to test. Just go into irb, and make an object. Any object. I picked an Array, but a string or a fixnum or even a class you made yourself will do. Try typing the name of the object and then class. As so
What does this mean? It means that if you use an Array you can use all the methods contained in both Object and BasicObject. Object contains many useful methods, like for example, class, which we just used. Which brings us to the next point of discussion, method calls. A method call is quite simply when you call an operation on an object (anything in ruby!) by using a period and then the command. What's interesting is what happens when you call a method on an object.
First ruby checks the class of the object in question and scans from top to bottom looking for the method in question. If it finds it, it runs the last instance of it found, if not it goes into whatever class we inherited from, all the way up to BasicObject. If it finds nothing, it returns an error!
Were you to run SampleClass.new.sample_method, you'd simply get an output of "this method is called", as opposed to "this method is not called" because ruby will always take the last definition. Similarly, if you made a class called say "SonClass" that inherited from "SampleClass" and tried to run sample_method on it, it would just grab it from SampleClass, unless that is, you defined sample method in SampleClass...
Its these properties that make ruby so modular, since you can open up Array and edit its internal functions, or even add functions that can be used by anyone calling on an Array...
The most important thing to get, and something that takes a while to get a handle on at first, is that in ruby, everything is an object. Everything. Not just the thing you made a class out of, but everything you use. When you define a variable, that variable points to an object. When you create an array, that array is an object.
More importantly, every object belongs to a class. Read that again. Every object belongs to a class. If you go far up the chain, every object actually inherits from the Object class, which in turn inherits from the BasicObject class. So really, when we say "everything in ruby is an object" we mean, "everything in ruby inherits from the Object class".
This is super easy to test. Just go into irb, and make an object. Any object. I picked an Array, but a string or a fixnum or even a class you made yourself will do. Try typing the name of the object and then class. As so
[].class
=> ArrayThen, add .superclass on top of the class method call.
[].class.superclass
=> ObjectDo it one more time
[].class.superclass.superclass
=> BasicObjectThis is as far down as the chain goes, if you do it one more time, you get "nil", which means there's no super super super class for array.
What does this mean? It means that if you use an Array you can use all the methods contained in both Object and BasicObject. Object contains many useful methods, like for example, class, which we just used. Which brings us to the next point of discussion, method calls. A method call is quite simply when you call an operation on an object (anything in ruby!) by using a period and then the command. What's interesting is what happens when you call a method on an object.
First ruby checks the class of the object in question and scans from top to bottom looking for the method in question. If it finds it, it runs the last instance of it found, if not it goes into whatever class we inherited from, all the way up to BasicObject. If it finds nothing, it returns an error!
Were you to run SampleClass.new.sample_method, you'd simply get an output of "this method is called", as opposed to "this method is not called" because ruby will always take the last definition. Similarly, if you made a class called say "SonClass" that inherited from "SampleClass" and tried to run sample_method on it, it would just grab it from SampleClass, unless that is, you defined sample method in SampleClass...
Its these properties that make ruby so modular, since you can open up Array and edit its internal functions, or even add functions that can be used by anyone calling on an Array...
Tuesday, September 6, 2016
HTML: Thinking In Boxes
Thinking In Boxes
One of the hardest things to comprehend when learning htlm and css is the transition between code and physical spacing. That is, how do a bunch of tags become a well designed website?
How does this happen?
It can be very difficult at first to conceptualize how a vertical sequential cascading style can be actually made into something like the google homepage. The key to doing this, is to learn to think in boxes.
Everything in html is built around a box, or if you prefer. a frame. Lets look at the google homepage for a moment. If you look at it broadly, it can be broken into three or four groupings, which in reality are boxes. You can easily verify what's grouped together in the google homepage, by simply going to it in your browser and zooming out. You'll notice there are certain areas which "cluster" together.
There is actually a fifth box to consider, the page itself, you should always remember that the page itself can be a defined frame for you to move things around in.
Knowing this, it is suddenly very easy to start figuring out what to code. For example, you might start with the upper right navigation bar. Now that you know that it's a box, you can code the things inside the box, style them, and then and only then worry about properly placing them. Since you know you need a box to place them in, you might define the whole page as a box with "width: 100%;" on your css, so that your main "box" adjusts to fit the size of the viewers screen. Then you can get to the nitty gritty of actually locating your box within the bigger box of the page, perhaps by floating it right.
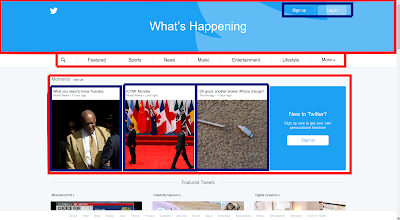
Lets look at another example. We'll go to twitter for this one. If you happen to be already logged on to twitter, I highly suggest visiting it in incognito mode on chrome so you get a chance to see what it looks like before we break it down into boxes.
It should be relatively easy to see here that we have boxes, and then boxes within boxes.
These are the outside boxes, a top login/logo container, with buttons, a navbar, and then a highlights section. From a UX point of view, it's quite elegant. As a beginner to html, it might give you conniptions however. The nav bar itself is fairly easy, but what about the login buttons on the "What's happening" section? Or the stuff in the moments box?
If we remember that we can place boxes within boxes, then it becomes a lot simpler.
Suddenly the moments section doesn't seem so difficult. We just need a heading, a subheading an image (which we need to remember to limit in size), and then we can place all that within a "moments" frame. If we make our individual moment boxes inline objects, and are careful with our spacing, it'll all stack neatly. By thinking of the individual moments as boxes, and then just treating them as single entities when they were done, we made a seemingly difficult task, into a relatively trivial one.
So, to recap, when you're trying to think in html, your first and most important step is to break down everything into boxes. If you need to make a mockup for a website, it can be as easy as opening your image editor of choice, and throwing up boxes to figure out your layout.
In particularly complex layouts you might wind up within boxes within boxes within boxes ad nauseam, but as long as you break the page down into its individual boxes, you should always be able to position things the way you want to.
Monday, August 22, 2016
AirBnB UX Teardown
AirBnB, an UX analysis.
UX, short for User eXperience, is basically, the science and art of designing web pages to best accommodate the users, and by extension, the interest of the business involved. There are a number of principles that go into UX, with the ultimate goal being to leave the user feeling like the website was accessible, useful and informative. The goal, the majority of times, is to leave the user feeling like they wish to return to the site.
The best way to understand the principles behind UX is to do a thorough examination of a website. If you're not familiar with the basics of UX, I suggest this article. It serves as a pretty thorough introduction, and is probably a better jumping off point than this blog post. Failing that, there's nothing like jumping right in.
The best way to start is by poking around the website, so I did just that, I spent a solid thirty minutes clicking things, and figuring out how to navigate the site. The key point was to think critically about what, as an user, I'd like to see and do. AirBnB is a website that caters to travelers and people with excess space looking to make money, the goal of AirBnB is to connect these people, basically allowing individuals to work as hotels, and allowing travelers to either get an authentic experience or save money, sometimes both. AirBnB provides both an unique service and an unique idea.
Now the core question, who uses this website? The kind of user will determine what priorities the designer has in designing the website. Given the size of AirBnB and the general novelty of the idea, the website can expect to find the following kinds of users:
AirBnB successfully catches your attention
Now the core question, who uses this website? The kind of user will determine what priorities the designer has in designing the website. Given the size of AirBnB and the general novelty of the idea, the website can expect to find the following kinds of users:
- The authentic traveler: People who wish to travel around and get the most "real" experience. Many of these will be first time users, visiting the website as a result of word of mouth or other advertising techniques. For this type of traveler, its important to convey information about how the arrangement works more than anything.
- The thrifty traveler, looking to save money by exploring alternatives to expensive hotels. For this type of traveler it is important to emphasize the price and the quality relative to hotels.
- The host that wants to put people up and make money on the side. These people will be curious about payouts and the details of arrangements between themselves, BnB and the visitor.
These are three very varied demographics, and attempting to cater to all three is both ambitious and absolutely essential for the product to succeed. At the end of the day, the client wants to walk away with either a stay booked or able to profit from having strangers stay at their house. This means that the presentation of information so that the client can make the most informed decisions is essential, as is not burdening clients with information that isn't relevant to their specific experience (e.g. the host probably doesn't care about how "real" the experience might be if they were to travel).
The website does this quite effectively, prompting you at first with information on what AirBnB does, in colorful, pastels that are bound to appeal to the whimsy of the more "authentic" traveler, while not discouraging the others. The site is further broken down into easily accessible sub-sites that allow you to find the specifics a client might be interested in. Taglines like "belong anywhere" or "see what you can earn" are designed to separate the users by their specific interests.
Targeted at specific needs.
Of note too is the subtle use of shading to make the button pop, while appearing almost 2D, and the effective use of whitespace and color to call your attention. The website is extremely aesthetically pleasing. Further, the use of pictures in the areas devoted to travelers serve to further guide the users attention in the desired manner. While the section aimed at hosting seems relatively small, it's very effective, as those seeking to host are likely less interested in being offered a plethora of options. There is room to argue that this plethora of choices may induce a form of click paralysis on users, but the shifting content and gorgeous pictures entice more than discourage.
For people searching, the information is clearly and prominently displayed, and the search results are concise. Its relatively easy to do both deep searches, and broad searches. The use of pictures is very effective, although the pop up asking you to log in can be a source of annoyance, especially the lack of a clear escape from it. Most first time users are probably not inclined to log in with facebook or google plus, and the prompt is kind of jarring.
Overall though, the site is incredibly polished, searches and favoriting things seems very intuitive, and there is a lot of information provided, crucially for travelers, pictures. The addition of a map, showing the exact location of places to stay is a welcome addition.
Overall, AirBnB is pretty darn effective, its clear a lot of thought and money went into designing the website, and its hard to find much fault without being nitpicky. The site keeps its users in mind, guarantees that they know where they are at all times (and can quickly return to the front page if they desire), and effectively serves their needs.
If you want to read a better teardown by someone who does this for a living, you can find Jason Shah teardown here. I highly suggest you read it.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)